Storage Layout¶
When configured as PersistentClient or running as a server, Chroma persists its data under the
provided persist_directory.
For PersistentClient the persistent directory is usually passed as path parameter when creating the client, if not
passed the default is ./chroma/ (relative path to where the client is started from).
For the server, the persistent directory can be passed as environment variable PERSIST_DIRECTORY or as a command line
argument --path. If not passed, the default is ./chroma/ (relative path to where the server is started).
Once the client or the server is started a basic directory structure is created under the persistent directory
containing the chroma.sqlite3 file. Once collections are created and data is added, subdirectories are created for
each collection. The subdirectories are UUID-named and refer to the vector segment.
Chroma Ops - Maintenance CLI
If you are looking maintenance CLI that can help you inspect, configure and improve the performance of your Chroma, try Chroma Ops.
Directory Structure¶
The following diagram represents a typical Chroma persistent directory structure:
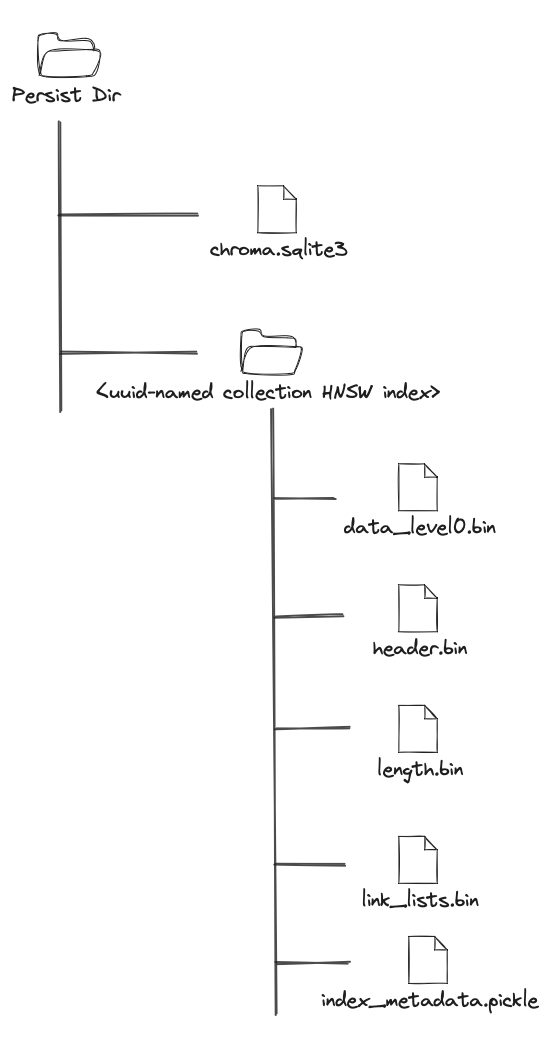
chroma.sqlite3¶
Note about the tables
While we try to make it as accurate as possible chroma data layout inside the slite3 database is subject to change.
The following description is valid as of version 0.5.0. The tables are also not representative of the distributed
architecture of Chroma.
The chroma.sqlite3 is typical for Chroma single-node. The file contains the following four types of data:
- Sysdb - Chroma system database, responsible for storing tenant, database, collection and segment information.
- WAL - the write-ahead log, which is used to ensure durability of the data.
- Metadata Segment - all metadata and documents stored in Chroma.
- Migrations - the database schema migration scripts.
- Collections - each collection has its own subdirectory, a UUIDv4-named diretory which stores HNSW index and its metadata.
Sysdb¶
The system database comprises the following tables:
tenants- contains all the tenants in the system. Usually gets initialized with a single tenant -default_tenant.databases- contains all the databases per tenant. Usually gets initialized with a single database -default_databaserelated to thedefault_tenant.collections- contains all the collections per database.collection_metadata- contains all the metadata associated with each collection. The metadata for a collection consists of any user-specified key-value pairs and thehnsw:*keys that store the HNSW index parameters.segments- contains all the segments per collection. Each collection gets two segments -metadataandvector.segment_metadata- contains all the metadata associated with each segment. This table containshnsw:*keys that store the HNSW index parameters for the vector segment.
WAL¶
The write-ahead log is a table that stores all the changes made to the database. It is used to ensure that the data is durable and can be recovered in case of a crash. The WAL is composed of the following tables:
embeddings_queue- contains all data ingested into Chroma. Each row of the table represents an operation upon a collection (add, update, delete, upsert). The row contains all the necessary information (embedding, document, metadata and associated relationship to a collection) to replay the operation and ensure data consistency.embeddings_queue_config- contains the configuration for the embedding queue. As of version0.6.3the configuration only pertains to automatic embedding queue purging.max_seq_id- maintains the maximum sequence ID of the metadata segment that is used as a WAL replay starting point for the metadata segment.
{
"automatically_purge": true,
"_type": "EmbeddingsQueueConfigurationInternal"
}
Metadata Segment¶
The metadata segment is a table that stores all the metadata and documents stored in Chroma. The metadata segment is composed of the following tables:
embeddings- contains embedding listings for all collections.embedding_metadata- contains all the metadata associated with each document and its embedding.embedding_fulltext_search- document full-text search index. This is a virtual table and upon inspection of the sqlite will appear as a series of tables starting withembedding_fulltext_search_. This is an FTS5 table and is used for full-text search queries on documents stored in Chroma (viawhere_documentfilter inqueryandgetmethods).
Migrations¶
The migrations table contains all schema migrations applied to the chroma.sqlite3 database. The table is used for tracking applied migrations.
Collection Subdirectories¶
Each collection has its own subdirectory, a UUIDv4-named diretory which stores HNSW index and its metadata.
header.bin- Holds metadata about the index, such as its parameters and structure details.length.bin- Records the number of links each node has, aiding in efficient traversal during searches.link_lists.bin- Stores the adjacency lists for nodes, detailing their connections within the graph.data_level0.bin- Contains the base layer of the hierarchical graph, storing the actual vectors and their connections.index_metadata.pickle- Chroma specific metadata about mapping between ids inembeddingstable and labels in the HNSW index.